Installing IDA Application on Java 8
Below are steps to install the IDA application on Java 8. Please note starting from version 25.0.3, IDA supports Spring Framework v6 based on Java 17, which is the recommended way to install the IDA application.
-
For installing IDA application on Java 17, see Installing IDA Application on Java 17(Recommended)
-
For installing applications of earlier versions of IDA, see Installing IDA Application(v3.x, v2.x)
The IDA Web Application can be installed on WebSphere Application Server (WAS), Liberty. Please access IDA web URLs using HTTPS.
Installing on Liberty
Prerequisites
- Java 8 is installed on server.
- Download Liberty installation package: Open Liberty v24.0.0.3+, WebSphere Liberty v24.0.0.3+.
1. Create a Liberty server
You can create a server from the command line.
-
Unzip the Liberty installation package. Open a command line, then navigate to the wlp/bin directory. Where
is the location you installed Liberty on your operating system. -
Run the following command to create a server.
<path_to_liberty>/wlp/bin/server create <SERVER_NAME>
The ‘SERVER_NAME’ must use only Unicode alphanumeric (for example, 0-9, a-z, A-Z), underscore (_), dash (-), plus (+), and period (.) characters. The name cannot begin with a dash or period. Your file system, operating system, or compressed file directory might impose more restrictions.
If the server is created successfully, you will receive the message: Server SERVER_NAME created.
2. Configure server.xml
Edit server.xml from <path_to_liberty>/wlp/usr/servers/<SERVER_NAME> folder. You could use the below sample server.xml to override your server.xml and update httpPort, httpsPort and keyStore password and enable features ssl, websocket.
IDA supports JNDI datasource. You can configure a data source and JDBC provider for database connectivity.
1. In the server.xml file, define a shared library that points to the location of your JDBC driver JAR or compressed files. For example:
<library id="DBLib">
<fileset dir="${shared.config.dir}/lib" includes="*.jar"/>
</library>
2. Configure attributes for the data source, such as JDBC vendor properties and connection pooling properties. For example:
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/ida">
<connectionManager maxPoolSize="50"/>
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="DBLib" />
<properties.postgresql serverName="localhost" portNumber="5432"
databaseName="idadb" user="idadbadmin" password="idadbadmin" />
</dataSource>
3. Support for X-Forwarded-* and Forwarded headers
Add the below configuration in server.xml to support X-Forwarded-* and Forwarded headers in Liberty, which means better integration with front-end HTTP load balancers and web servers.
<httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint"
host="*" httpPort="-1"
httpsPort="9443">
<remoteIp useRemoteIpInAccessLog="true"/>
</httpEndpoint>
Here is a sample server.xml
Please update the fields host, httpPort, and httpsPort, library, and dataSource. For more information about configuring relational database connectivity in Liberty, please refer to Data Source Configuration.
For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<server description="new server">
<!-- Enable features -->
<featureManager>
<feature>servlet-3.1</feature>
<feature>transportSecurity-1.0</feature>
<feature>websocket-1.1</feature>
<feature>jdbc-4.2</feature>
<feature>jndi-1.0</feature>
</featureManager>
<!-- This template enables security. To get the full use of all the capabilities, a keystore and user registry are required. -->
<!-- For the keystore, default keys are generated and stored in a keystore. To provide the keystore password, generate an
encoded password using bin/securityUtility encode and add it below in the password attribute of the keyStore element.
Then uncomment the keyStore element. -->
<keyStore id="defaultKeyStore" password="idaAdmin" />
<!-- There's an issue using JDK 8 with TLSv1.3, enable TLSv1.2 as below to work around the issue. -->
<ssl id="defaultSSLConfig" keyStoreRef="defaultKeyStore" trustDefaultCerts="true" sslProtocol="TLSv1.2"/>
<webContainer invokeFlushAfterService="false"/>
<!--For a user registry configuration, configure your user registry. For example, configure a basic user registry using the
basicRegistry element. Specify your own user name below in the name attribute of the user element. For the password,
generate an encoded password using bin/securityUtility encode and add it in the password attribute of the user element.
Then uncomment the user element. -->
<basicRegistry id="basic" realm="BasicRealm">
<!-- <user name="yourUserName" password="" /> -->
</basicRegistry>
<!-- To access this server from a remote client add a host attribute to the following element, e.g. host="*" -->
<httpSession cookieSameSite="None"/>
<httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint"
host="*" httpPort="-1"
httpsPort="9443">
<remoteIp useRemoteIpInAccessLog="true"/>
</httpEndpoint>
<!-- Automatically expand WAR files and EAR files -->
<applicationManager autoExpand="true" startTimeout="360s" stopTimeout="120s"/>
<application type="war" id="ida" name="ida" location="${server.config.dir}/apps/ida-web.war">
<classloader delegation="parentLast" />
</application>
<!-- Shared libraries
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSEQTP_liberty/com.ibm.websphere.wlp.doc/ae/cwlp_sharedlibrary.html
-->
<!-- JNDI data source configuration -->
<!-- Define a shared library pointing to the location of the JDBC driver JAR or compressed files. For example: -->
<!-- PostgreSQL Example-->
<library id="PostgresSQLLib">
<fileset dir="${shared.config.dir}/lib/global" includes="postgresql-42.2.8.jar"/>
</library>
<!-- Configure attributes for the data source, such as JDBC vendor properties and connection pooling properties. For example: -->
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/ida">
<connectionManager maxPoolSize="50"/>
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="PostgresSQLLib" />
<properties.postgresql serverName="localhost" portNumber="5432"
databaseName="idadb" user="idadbadmin" password="idadbadmin" />
</dataSource>
<!-- PostgreSQL Example End-->
<!-- DB2 Example-->
<library id="DB2Lib">
<fileset dir="${shared.config.dir}/lib/global" includes="db2jcc4-11.1.jar"/>
</library>
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/ida" statementCacheSize="60" id="DB2DataSource"
isolationLevel="TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED" type="javax.sql.DataSource" transactional="true">
<connectionManager maxPoolSize="50"/>
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="DB2Lib"/>
<properties.db2.jcc databaseName="${env.DATABASE_NAME}" currentSchema="${env.CURRENT_SCHEMA}"
serverName="${env.DATABASE_SERVER_NAME}" portNumber="${env.DATABASE_PORT_NUMBER}"
user="${env.DATABASE_USER}" password="${env.DATABASE_PASSWORD}"/>
</dataSource>
<!-- DB2 Example End-->
<!-- Oracle Example-->
<library id="ORACLELib">
<fileset dir="${shared.config.dir}/lib/global" includes="ojdbc8-12.2.0.1.jar"/>
</library>
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/ida" statementCacheSize="60" id="OracleDataSource" isolationLevel="TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED" type="javax.sql.DataSource" transactional="true">
<connectionManager maxPoolSize="50"/>
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="ORACLELib"/>
<properties.oracle url="${env.DATABASE_URL}"
user="${env.DATABASE_USER}" password="${env.DATABASE_PASSWORD}"/>
</dataSource>
<!-- Oracle Example END-->
<!-- MySQL Example-->
<library id="MYSQLLib">
<fileset dir="${shared.config.dir}/lib/global" includes="mysql-connector-java-8.0.18.jar"/>
</library>
<!-- Configure attributes for the data source, such as JDBC vendor properties and connection pooling properties. For example: -->
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/ida" statementCacheSize="60" id="DefaultDataSource"
isolationLevel="TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED" type="javax.sql.DataSource" transactional="true">
<connectionManager maxPoolSize="50"/>
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="MYSQLLib"/>
<properties databaseName="<DATABASE_NAME>"
serverName="<SERVER_NAME>" portNumber="<SERVER_PORT>"
user="<USER_NAME>" password="<PASSWORD>"/>
</dataSource>
<!-- MySQL Example End-->
</server>
We found an issue using JDK 8 with TLSv1.3, which can cause very high CPU usage of IDA. To fix the issue, use TLSv1.2 by adding the below configuration to server.xml.
<ssl id="defaultSSLConfig" keyStoreRef="defaultKeyStore" trustDefaultCerts="true" sslProtocol="TLSv1.2"/>
Liberty supports Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption for passwords that are stored in the server.xml file. In the Liberty installation bin folder, you can use the securityUtility command to encrypt your password.
./securityUtility encode password
For more information about encryption, please refer to SecurityUtility Command.
If the database requires an SSL connection, set it in the datasource prop, for example, for DB2:
<properties.db2.jcc databaseName="${env.DATABASE_NAME}" currentSchema="${env.CURRENT_SCHEMA}"
serverName="${env.DATABASE_SERVER_NAME}" portNumber="${env.DATABASE_PORT_NUMBER}"
user="${env.DATABASE_USER}" password="${env.DATABASE_PASSWORD}" sslConnection="true"/>
Refer to Database connections with TLS.
3. Configure jvm.options
Create jvm.options from <path_to_liberty>/wlp/usr/servers/<SERVER_NAME> directory.
Set the maximum heap size to 8192m. If the heap size is not big enough, IDA checkstyle may crash with an out-of-memory exception thrown. Increasing the heap size and restarting the server can fix this issue.
-Xms512m
-Xmx8192m
You might also need to set a proxy server, then add the following lines to jvm.options based on your actual proxy setting.
-Dhttps.proxyHost=host
-Dhttps.proxyPort=port
-Dhttps=proxyUser=user
-Dhttps.proxyPassword=your password
4. Configure server.env (Optional)
Create server.env from <path_to_liberty>/wlp/usr/servers/<SERVER_NAME> directory.
The default IDA data folder is /var/ida/data. If the default value is not writable or not applicable, then add the following environment variable to server.env for your IDA data folder:
ENGINE_CONFIG_DATA_DIR=<your_ida_data_path>
5. Copy the ida-web.war to the apps directory
Copy the ida-web.war to <path_to_liberty>/wlp/usr/servers/<SERVER_NAME>/apps directory.
6. Start the Liberty server
<path_to_liberty>/wlp/bin/server start SERVER_NAME
7. Access IDA web application using HTTPS, for example, https://<IDA_HOST>:9443/ida
Installing on WAS V9
Check the WAS version
IDA uses the Spring Boot websocket feature, which is not supported by WebSphere v8.5.5. It is recommended to install IDA on WebSphere v9.0.5.4+.
- Login to the WAS console, in the Welcome part, you can see the version of WAS.
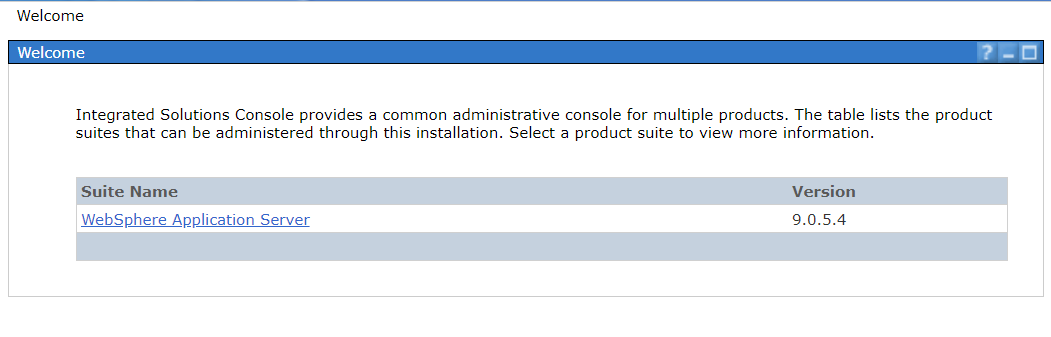
- If the WAS version is below 9.0.5.4, you should install the Fix Packs 9.0.5.4+, here is the minimum fix pack version:
-
Follow the instructions on this page to install the fix pack.
- When finished with the fix packs installation, the version will change to 9.0.5.4.
Update Session Management on WAS Console
-
Login to the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console as an administrator (URL: https://host:port/ibm/console/login.do?action=secure).
-
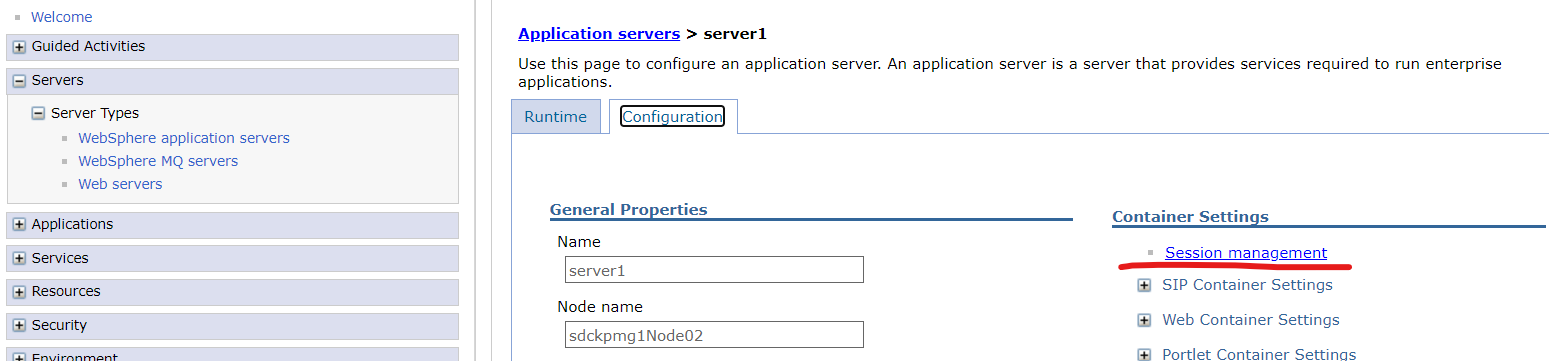
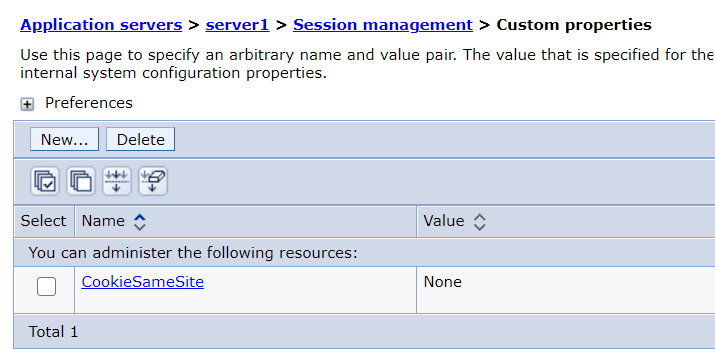
In the left navigation bar, click the Servers > Server Types > WebSphere application servers > server_name > Session management
-
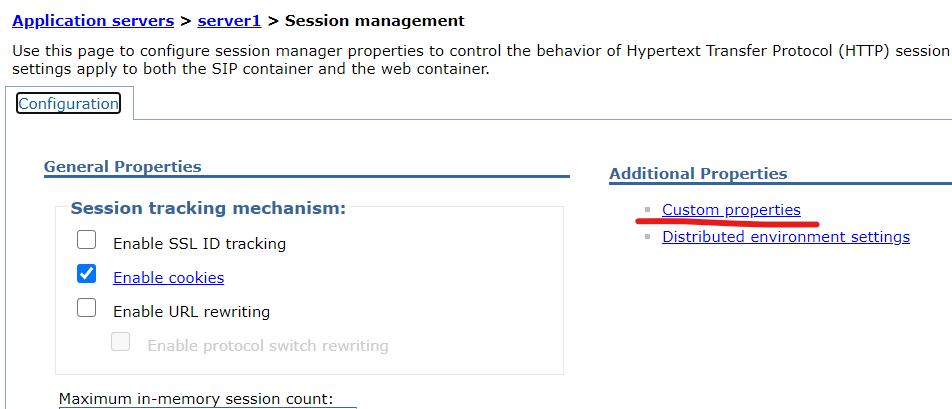
Add the ‘CookieSameSite’ custom property and set the value to ‘None’.
-
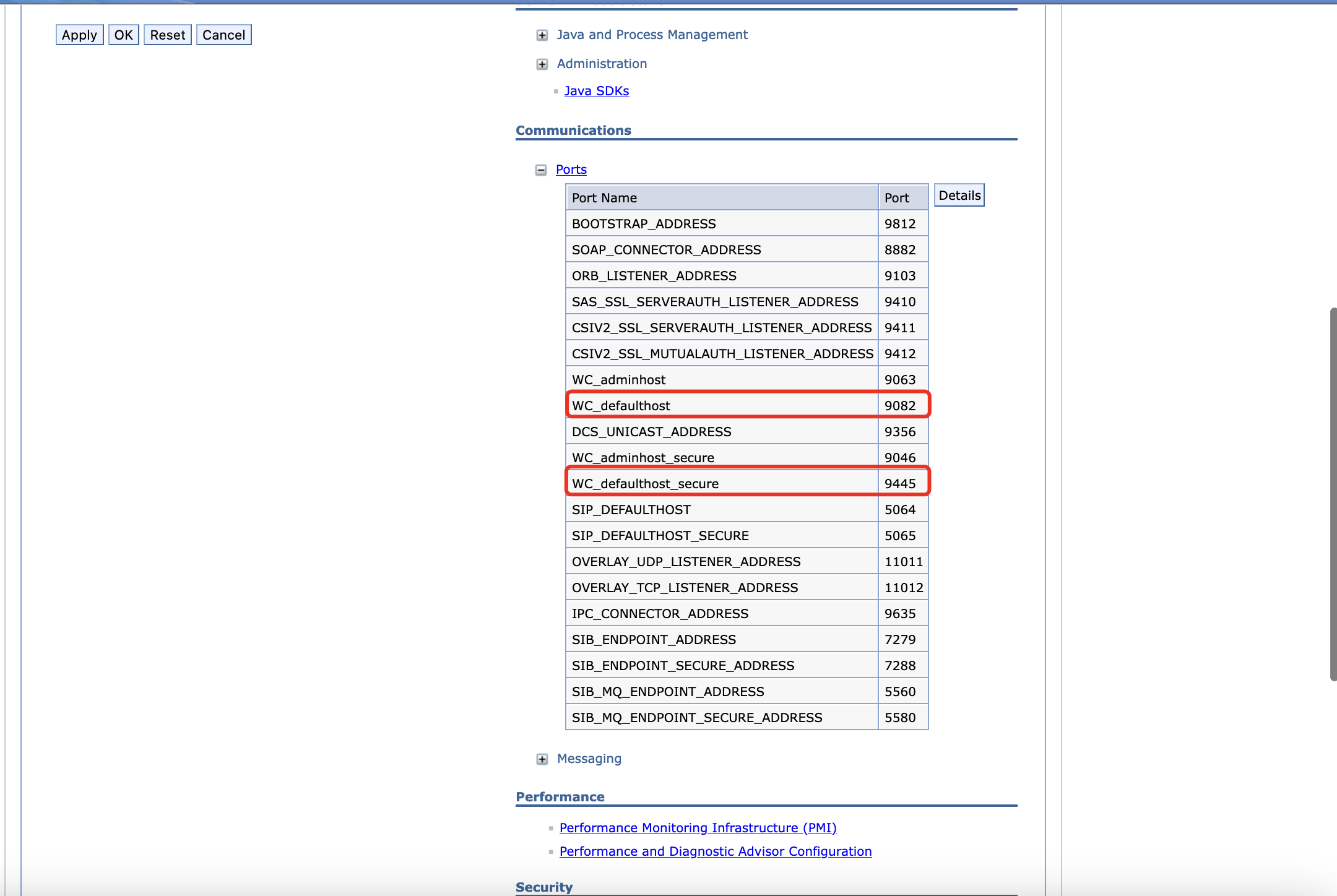
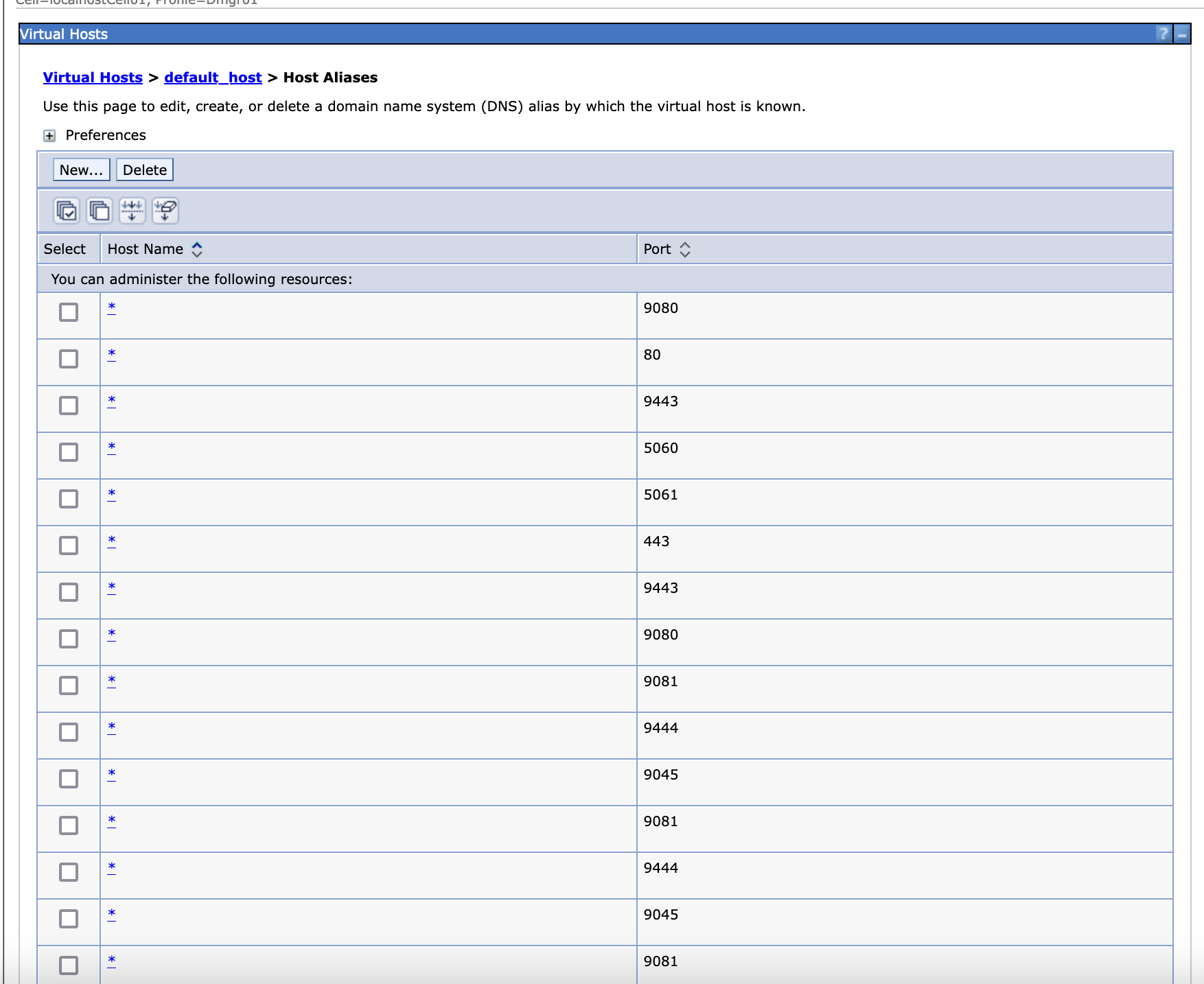
Make sure the host ports have been added to the Environment > Virtual hosts > default_host.
Setting environment entries on WAS Console (Optional)
The default IDA data folder is /var/ida/data. If the default value is not writable or not applicable, then follow the below steps to change the IDA data folder:
-
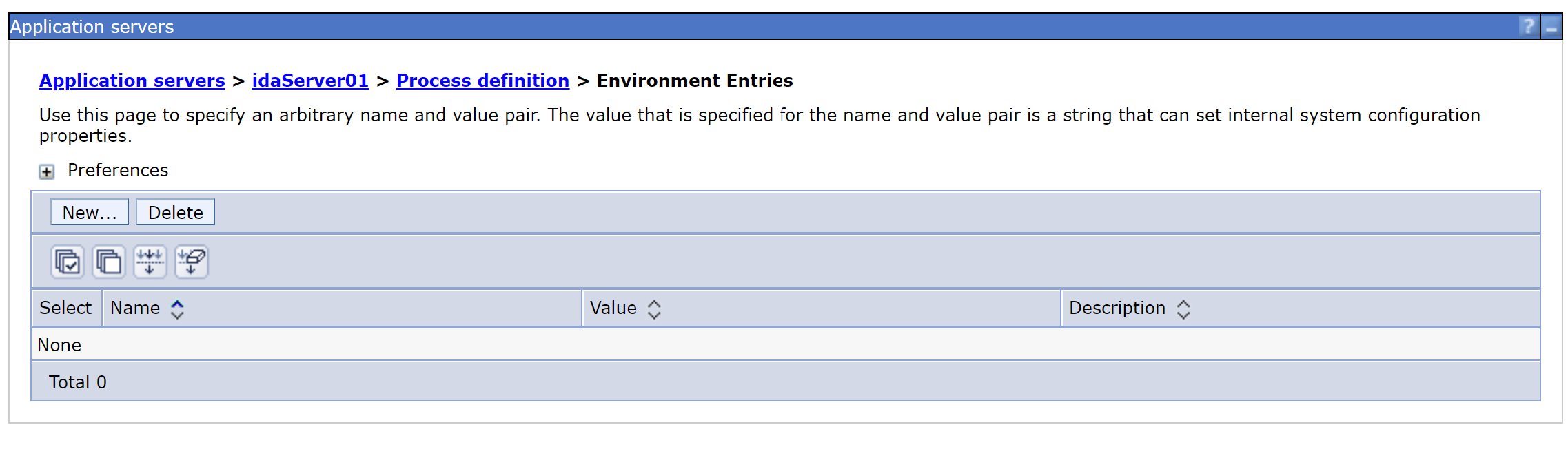
In the left navigation bar, click the Servers > Server Types > WebSphere application servers > server_name > Java and Process Management > Process Definition > Environment Entries > New
-
Add entries to the Name/Value pairs.
# IDA working directory data path # Ensure the path exists and the user running IDA has read/write permissions on the folder. ENGINE_CONFIG_DATA_DIR=/var/ida/data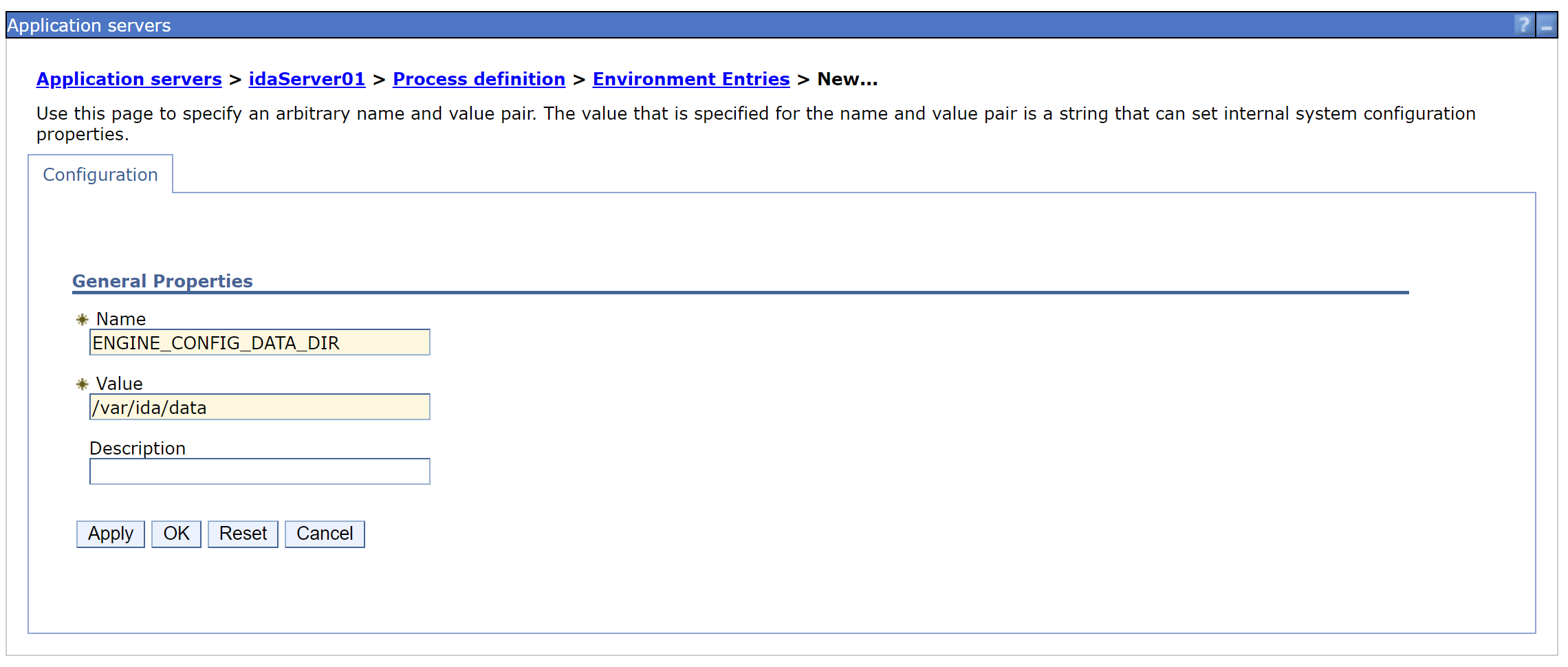
-
Click OK to save changes and restart the server.
Configure the JNDI
-
In the left navigation bar, click the Resource > JDBC > Data sources, and select the Node=< NODE_NAME >, Server=< SERVER_NAME > server scope.
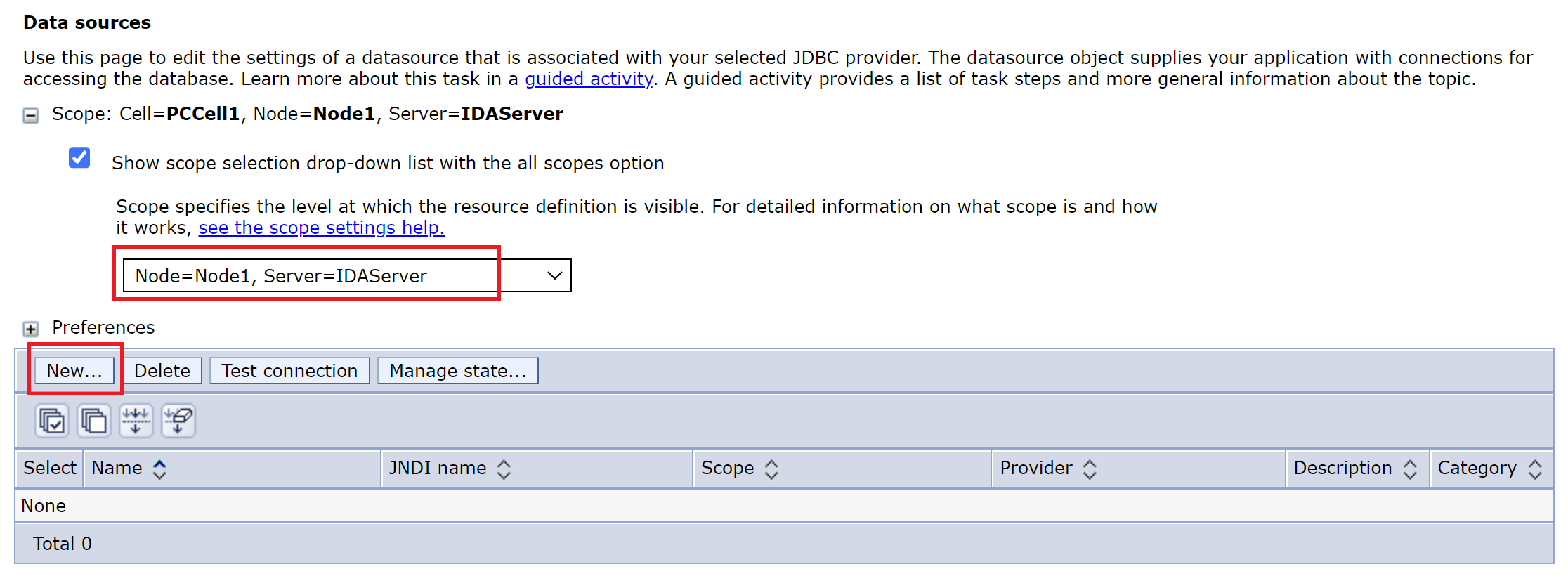
-
Create a new data source, we use DB2 as an example.
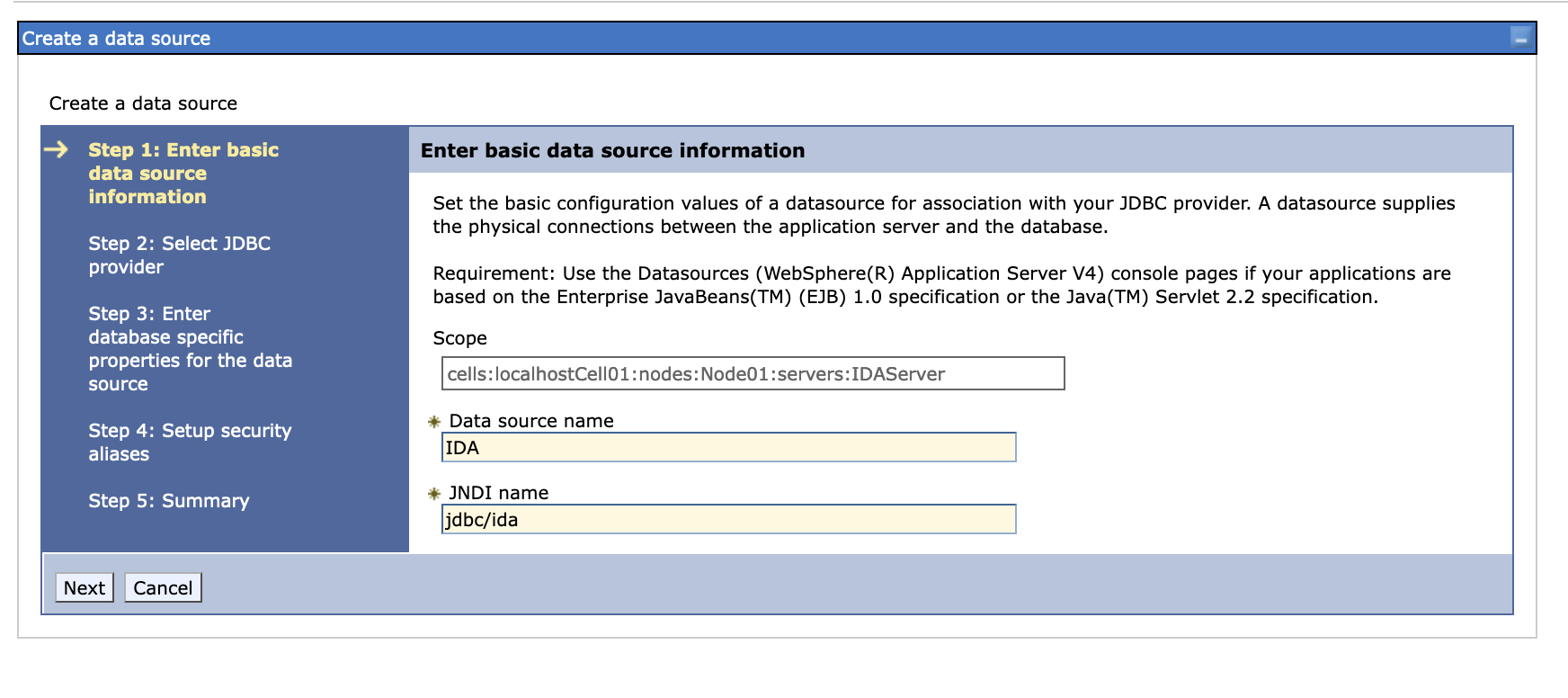
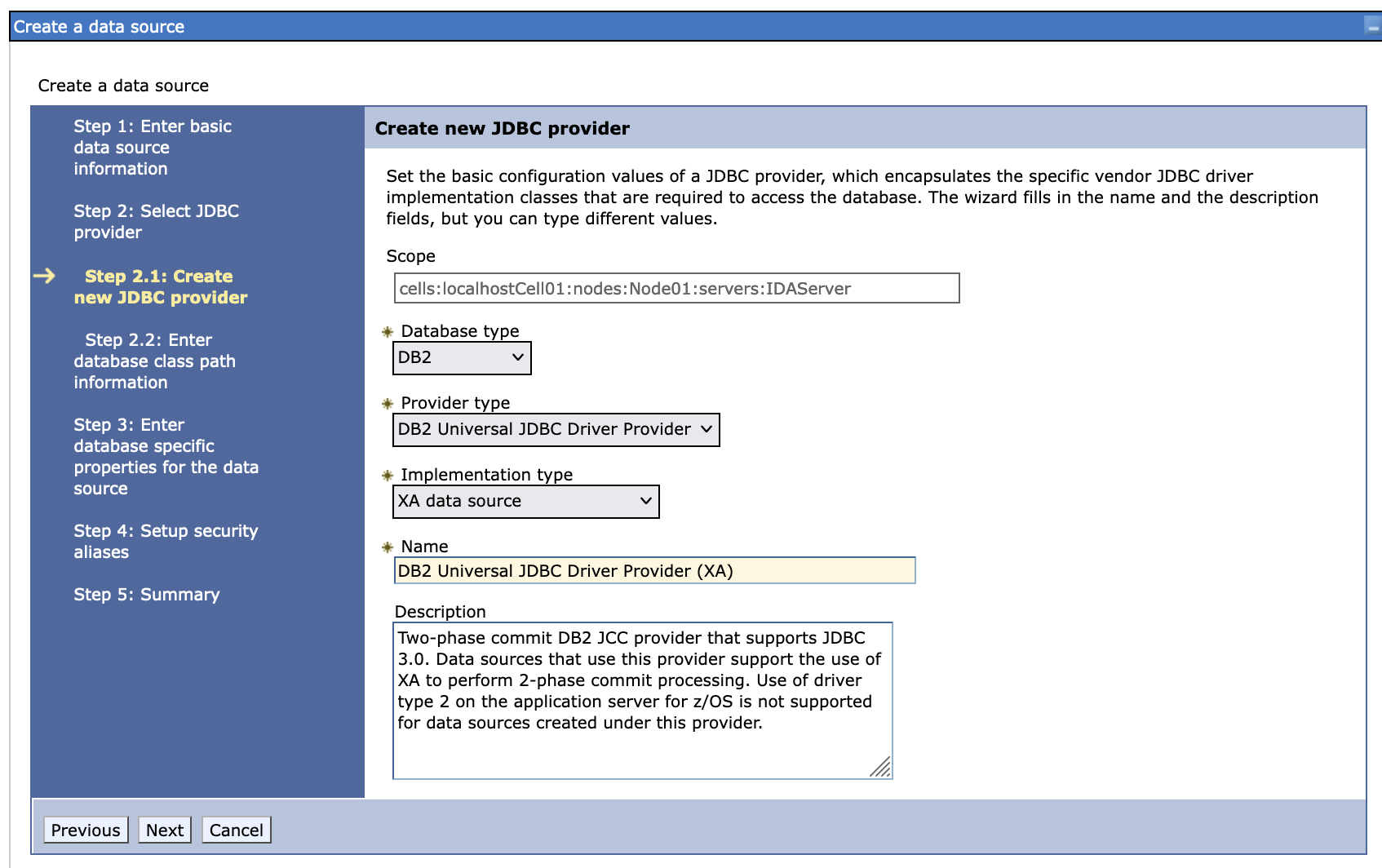
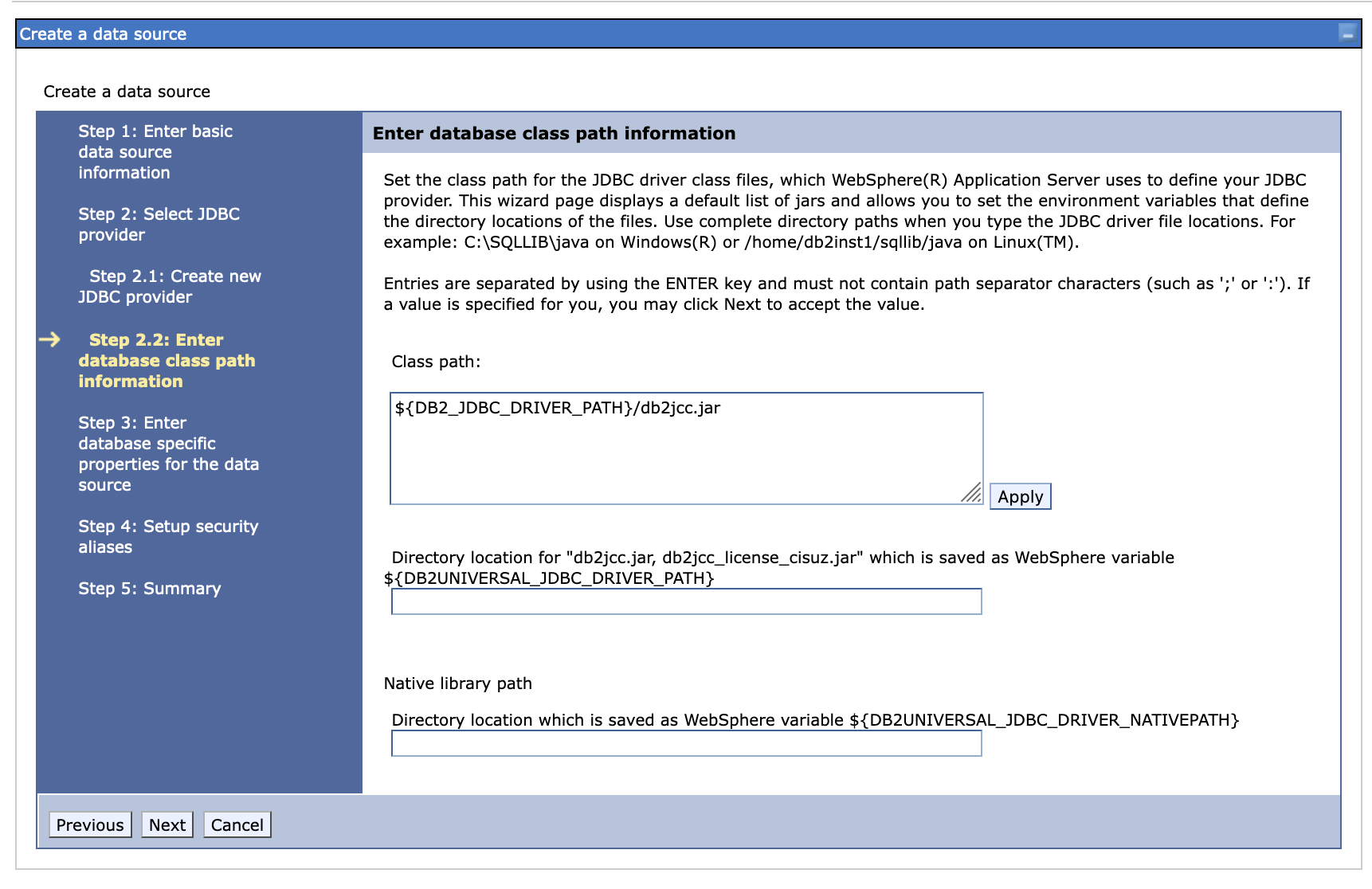
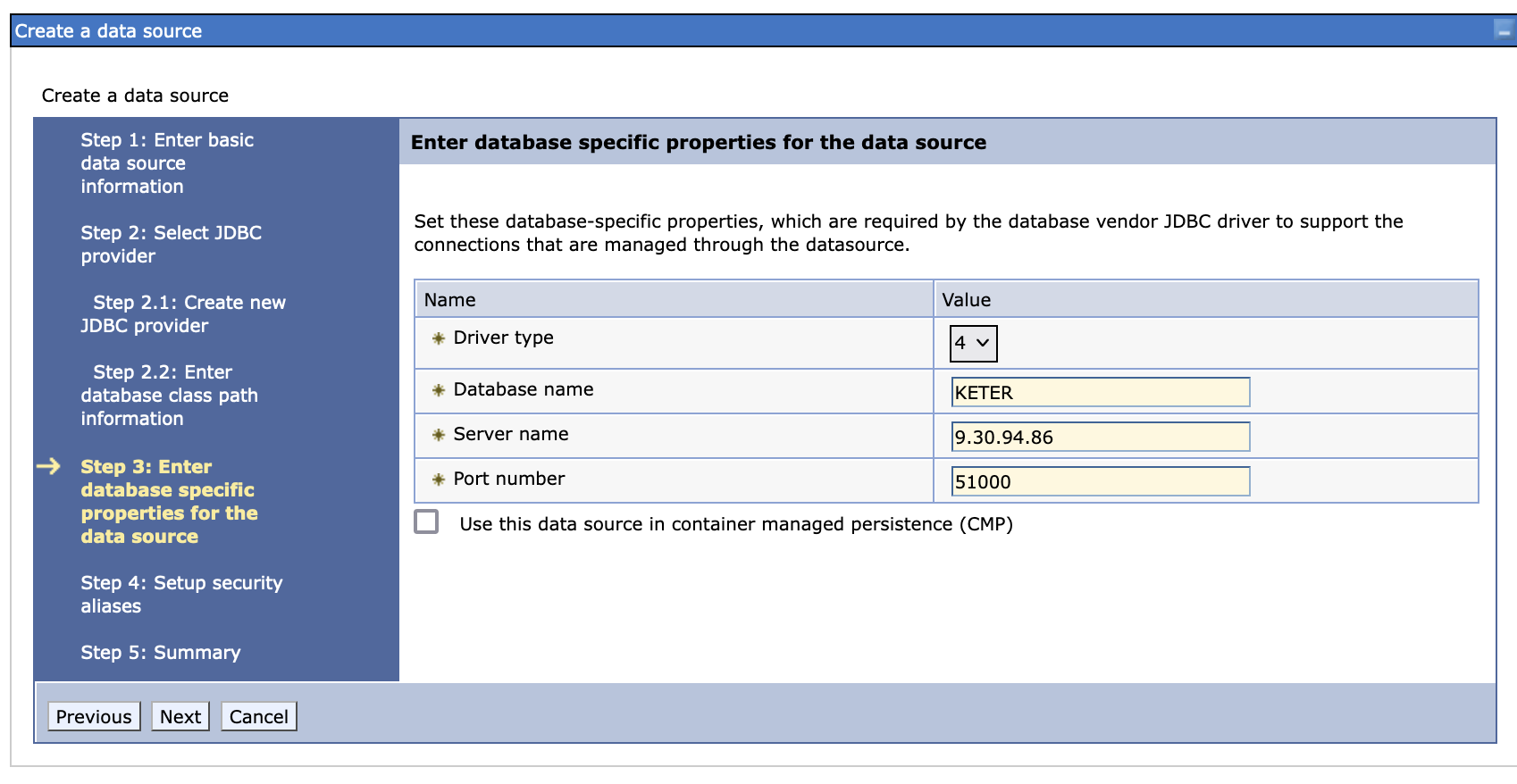
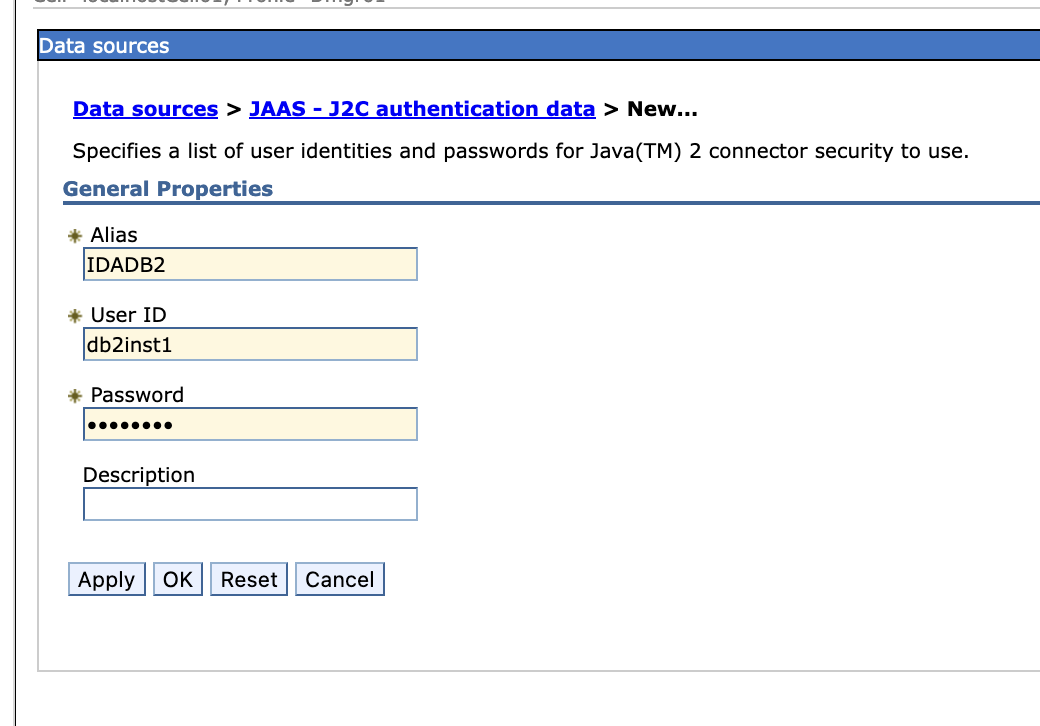
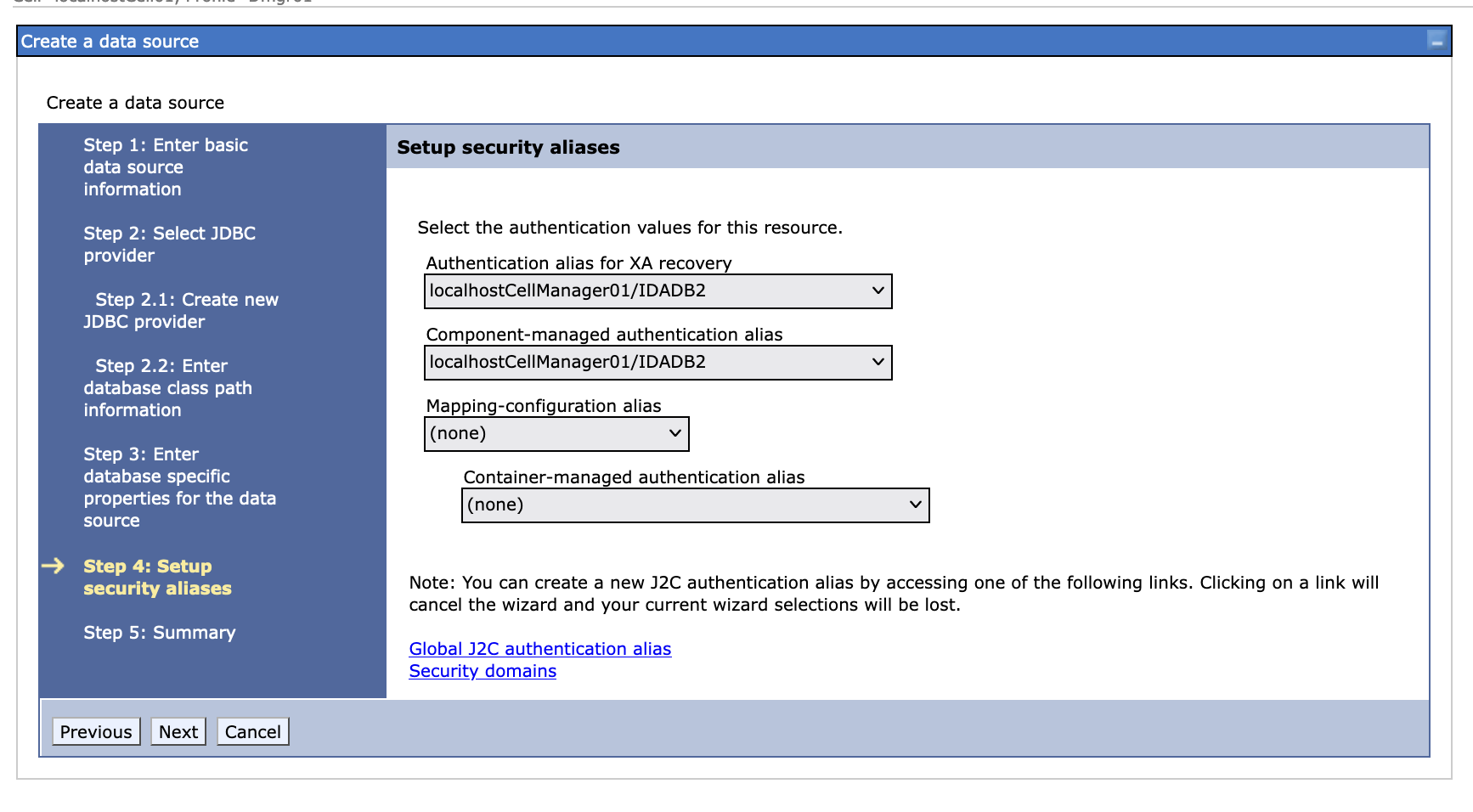
-
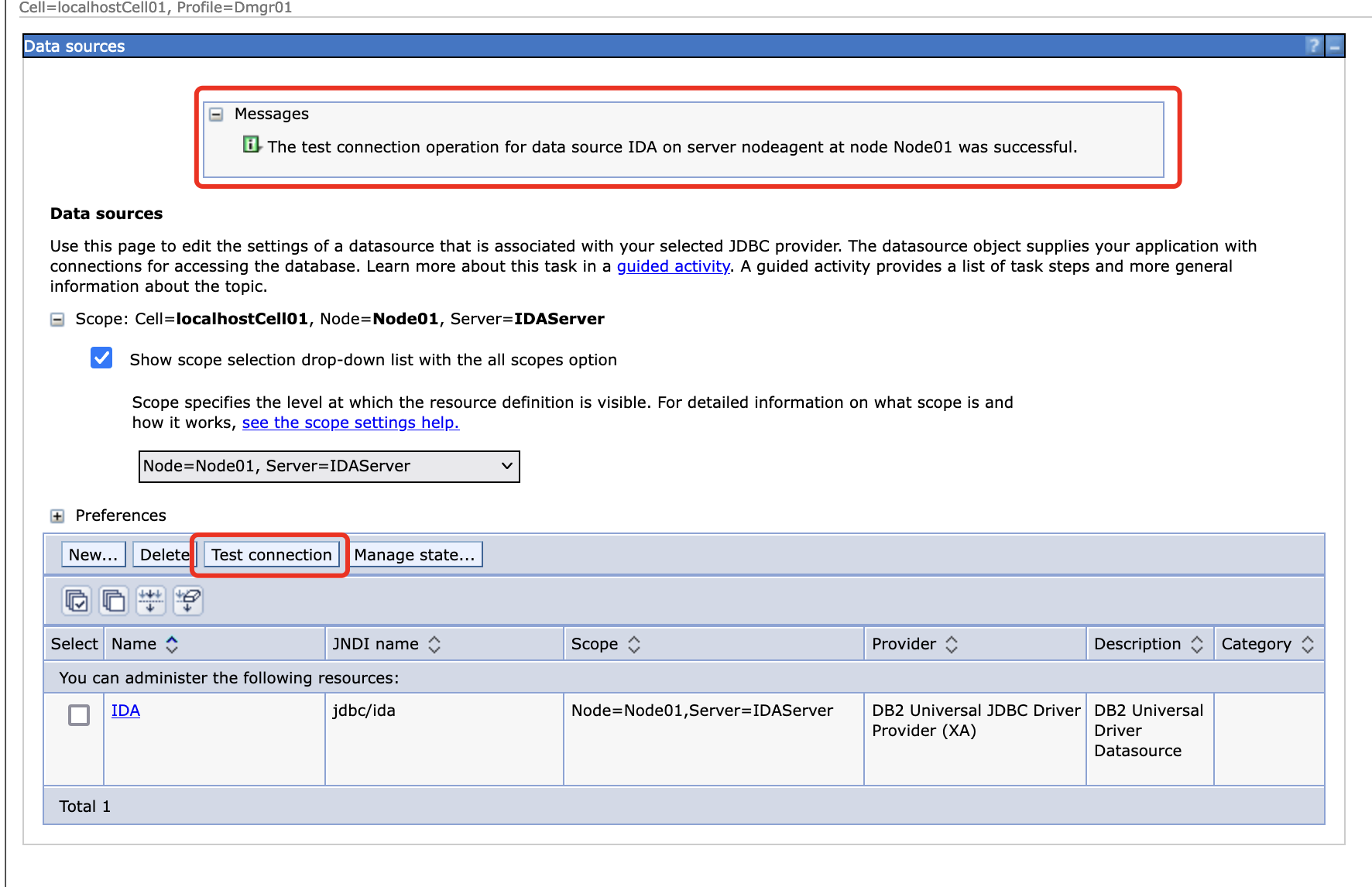
Test the connection for this data source, make sure this connection is successful.
Deploy a New Application on WAS
After finishing the installation of the fix packs, the next step is to deploy the IDA war to WAS.
-
Login to the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console as an administrator (URL: https://host:port/ibm/console/login.do?action=secure).
-
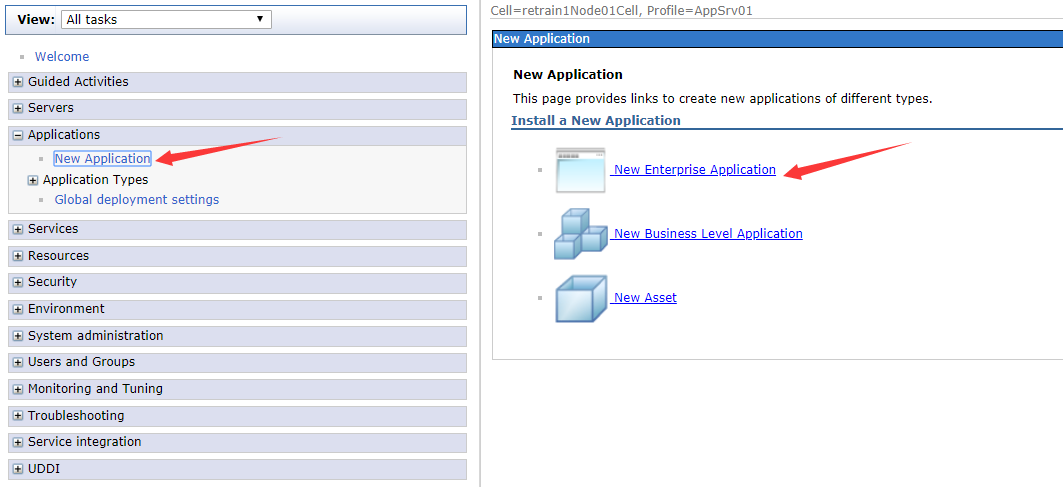
In the left navigation bar, click the New Application»New Enterprise Application.
-
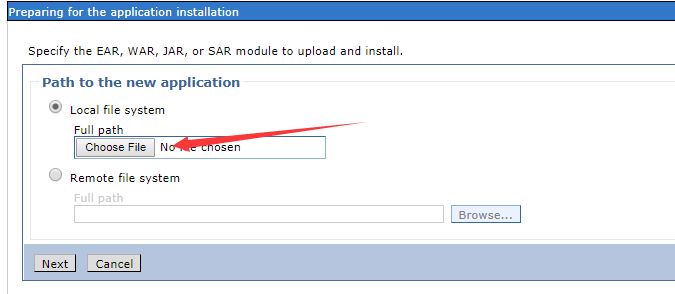
In the Path to the new application section, check the Local file system and select the ida-web.war in your local file system. When the war package is uploaded, click the Next button.
-
Choose the Fast Path option. Click the Next button.
-
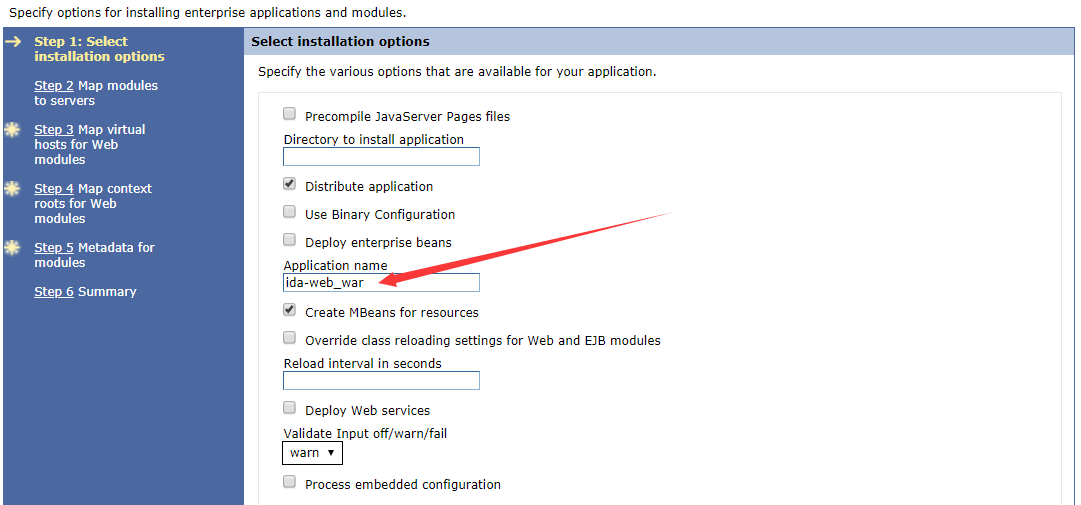
Now the current page is used to specify options for installing the enterprise application and modules. In step 1, you can change the application name, click the Next button after changing the application name.
-
There is nothing to change in step 2 and step 3. And step 4 is used to configure values for context roots in web modules, we should set the Context Root as /ida as shown below.
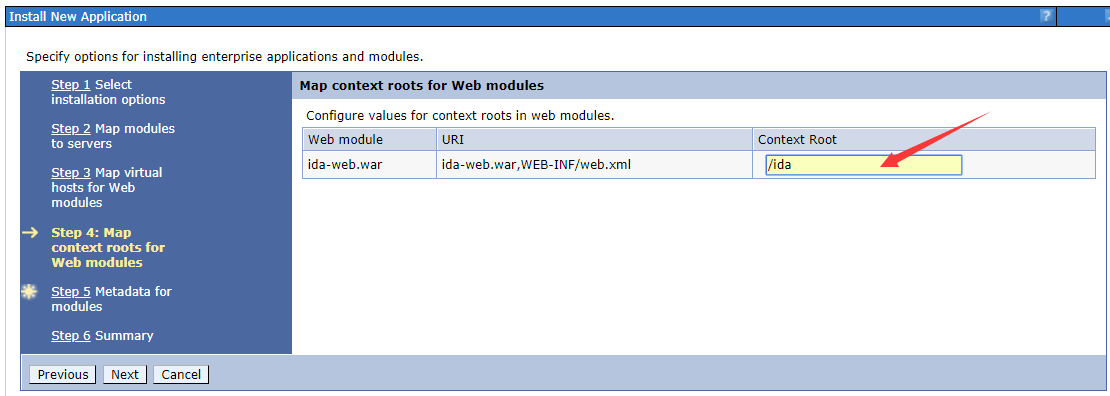
-
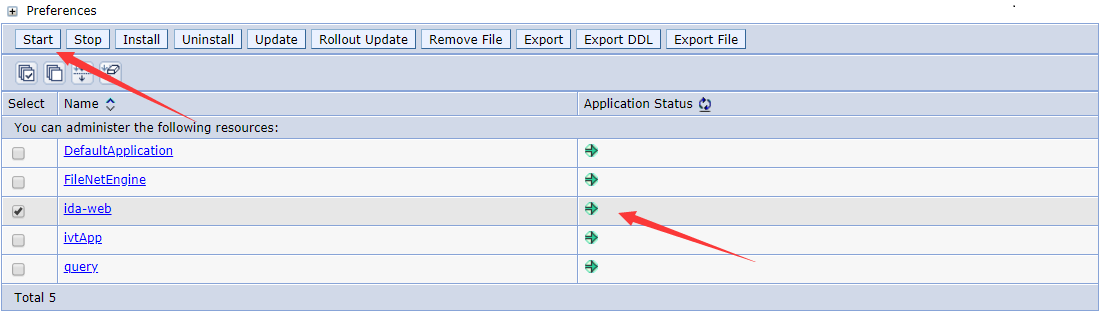
There is nothing to change in step 5. In step 6, click the Finish button and wait for the server to complete the installation of the IDA web application. When finished, click the WebSphere enterprise application in the left navigation bar, you can see that the IDA web application is in the Enterprise Applications table.
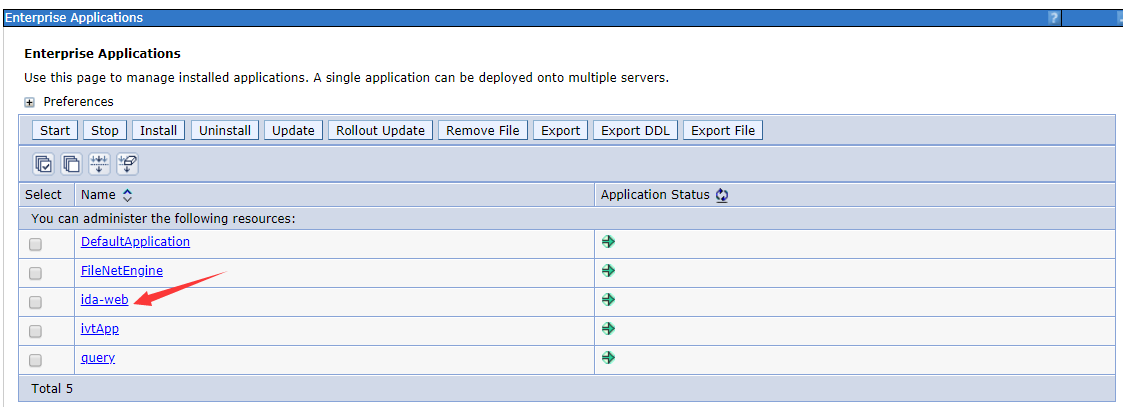
Configure the Class Loader Order
-
Click the link of the ida-web in the table and go to the app configuration page.
-
Click the Class loading and update detection link as shown below.
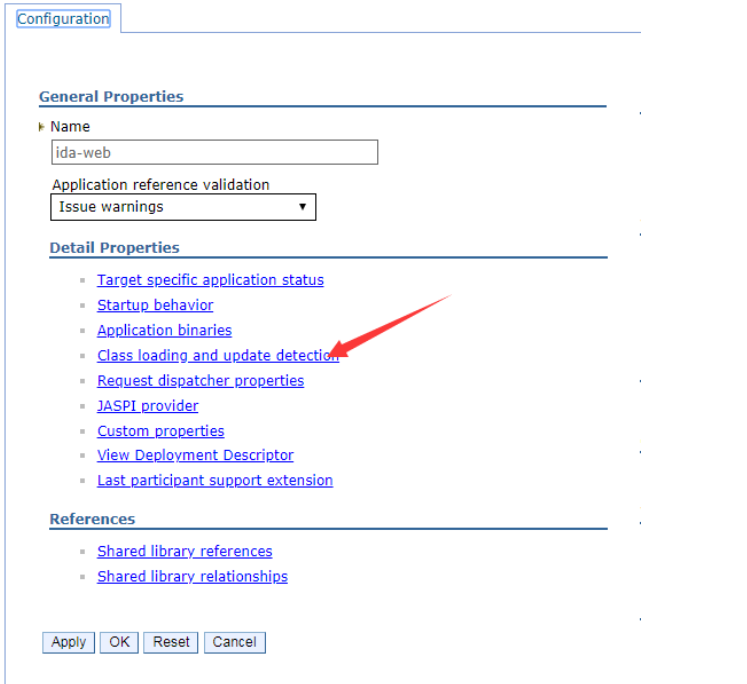
-
Change the class loader order to Classes loaded with local class loader first (parent last).
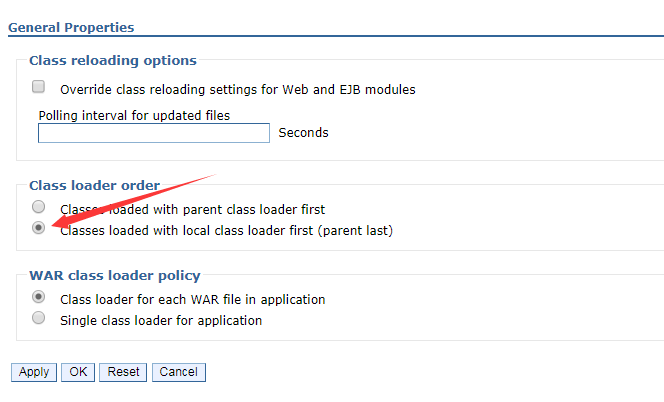
-
Then go back to the configuration page, and then click the Manage Modules link.
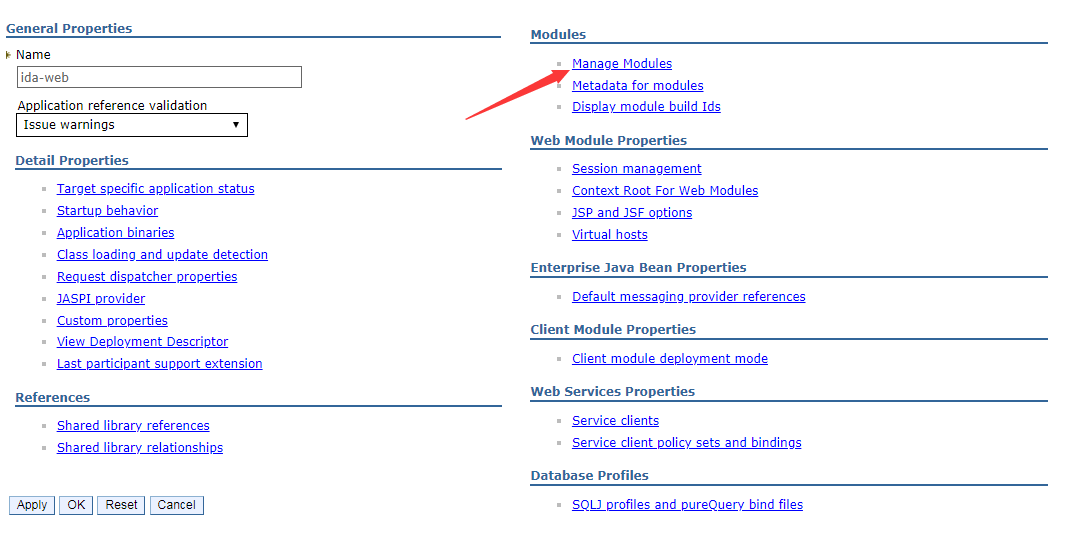
-
Click the link of ida-web.war, in the configuration page, change the class loader order to Classes loaded with local class loader first (parent last).
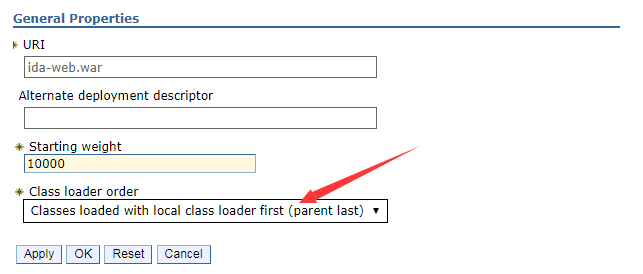
-
Save the changes and start the IDA web application. When the status of the IDA web application changes to started, you can visit the URL like https://<IDA_HOST>:<HTTPS_PORT>/ida to access the IDA web application.